2025 Standards Snapshot
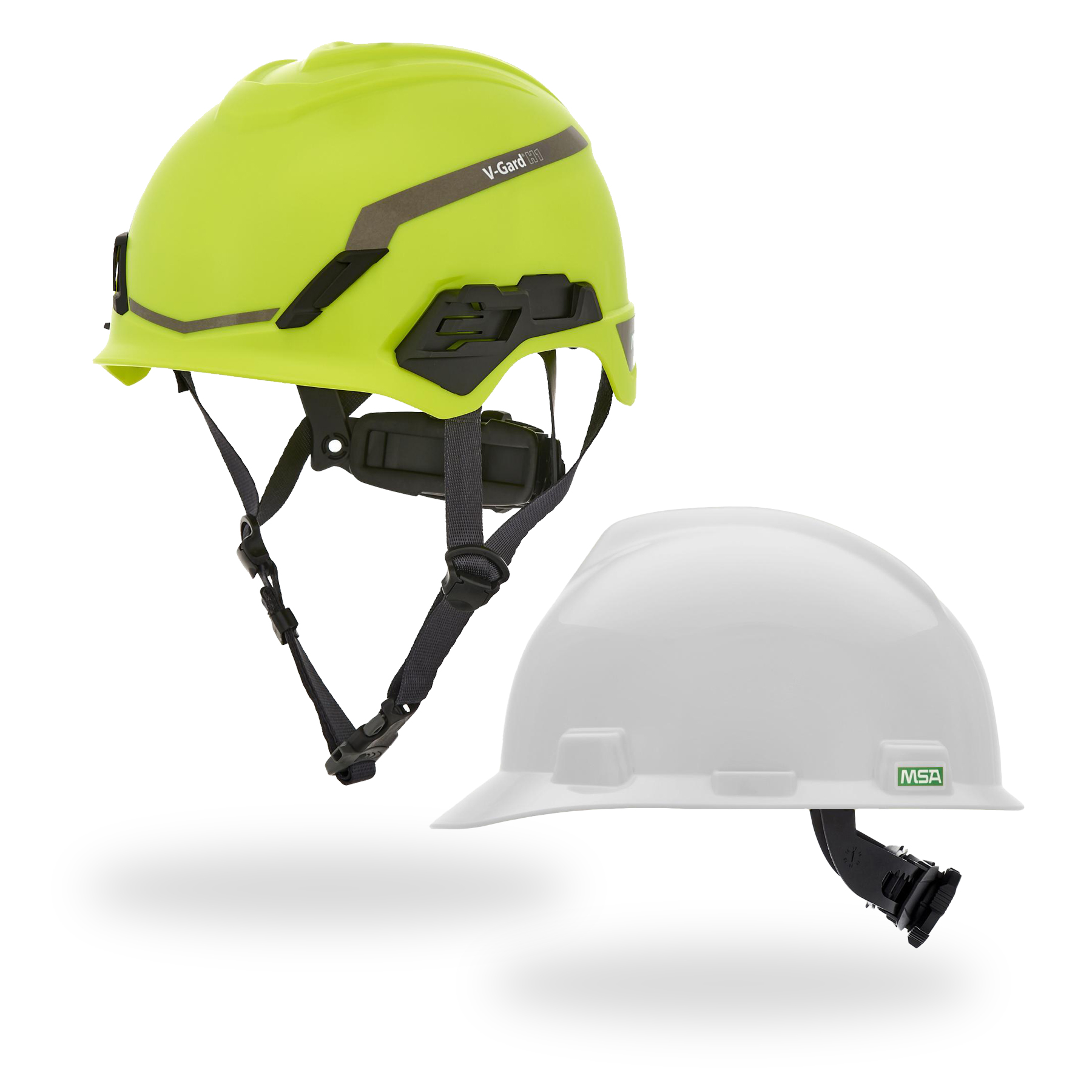
Helmet Types
- Type I – designed to protect from impacts to the top of the head
- Type II – protects from both top and side (lateral) impacts
Electrical Classes
- Class E – up to 20kV of protection
- Class G – up to 2.2kV of protection
- Class C – no electrical insulation
Testing Basics
Helmets are tested for impact force transmission, apex penetration resistance, and flammability. Type II helmets also undergo side-impact testing and chin strap retention checks to ensure straps stay secure and don’t overstretch.
Optional Ratings
Look for additional ratings when selecting head protection:
- LT/HT – performance in extreme low or high temperatures
- Reverse donning – approved for wearing backwards
- Enhanced visibility (EV) – bright, high-visibility colors
Bump Caps (ANSI/ISEA 100-2024)
A new standard sets minimum requirements for bump caps and requires a clear warning: “Not an industrial safety helmet.” These are only for minor, worker-generated knocks and must never replace a true safety helmet.
What’s Coming in 2025
Standards are evolving. Expect:
- A new Type I+ option, aligned with EN12492 to address off-crown impacts
- Updated chin strap performance requirements
- Visibility terms brought into alignment with ANSI/ISEA 107
The right choice of head protection depends on hazards, environment, and whether the helmet will stay on and perform under real conditions—slips, trips, side impacts, heat, and add on accessories your crews use.
How to pick the right head protection
Start with a quick hazard review and build a simple, enforceable spec.
1. Look at your hazards & applications
- Heights and the chance of slips, trips, or falls
- Moving loads/forklifts and side‑impact exposure
- Electrical work (decide E/G/C class)
- Risk of heat stress (venting, full brim, cooling)
- Chemicals, welding/arc, or confined spaces
2. Choose style & compatibility
- Cap vs. full brim; vented (for heat) vs. non‑vented (for electrical)
- Side rails and adapters for visors, earmuffs, lights so workers don’t remove PPE to make things fit
3. Other factors to consider
- Third party‑ certification, comfort, sweat management, low ride height
- Rotational impact features (where slips/angled impacts are likely)
- Logo/reflective customization for visibility and role ID
Testing, translated
In Z89.1-2014, helmets must limit how much force reaches the head form and prevent penetrators from contacting the “skull.” Type II adds off ‑center impact and penetration tests around the shell. If a chin strap is provided, retention is tested—it must stay attached and resist elongation. Optional LT/HT conditioning proves performance in extreme cold/heat; reverse ‑donning confirms the helmet can be worn backward safely.
Rotational Impact and Why Chin Straps Matter
Most falls and “struck by” events aren’t straight down hits. The head twists and slides — rotational motion that’s been directly linked to brain trauma. That’s why Type II helmets, paired with a properly adjusted chin strap, should be the smart default any time there’s risk of side impact or losing balance.
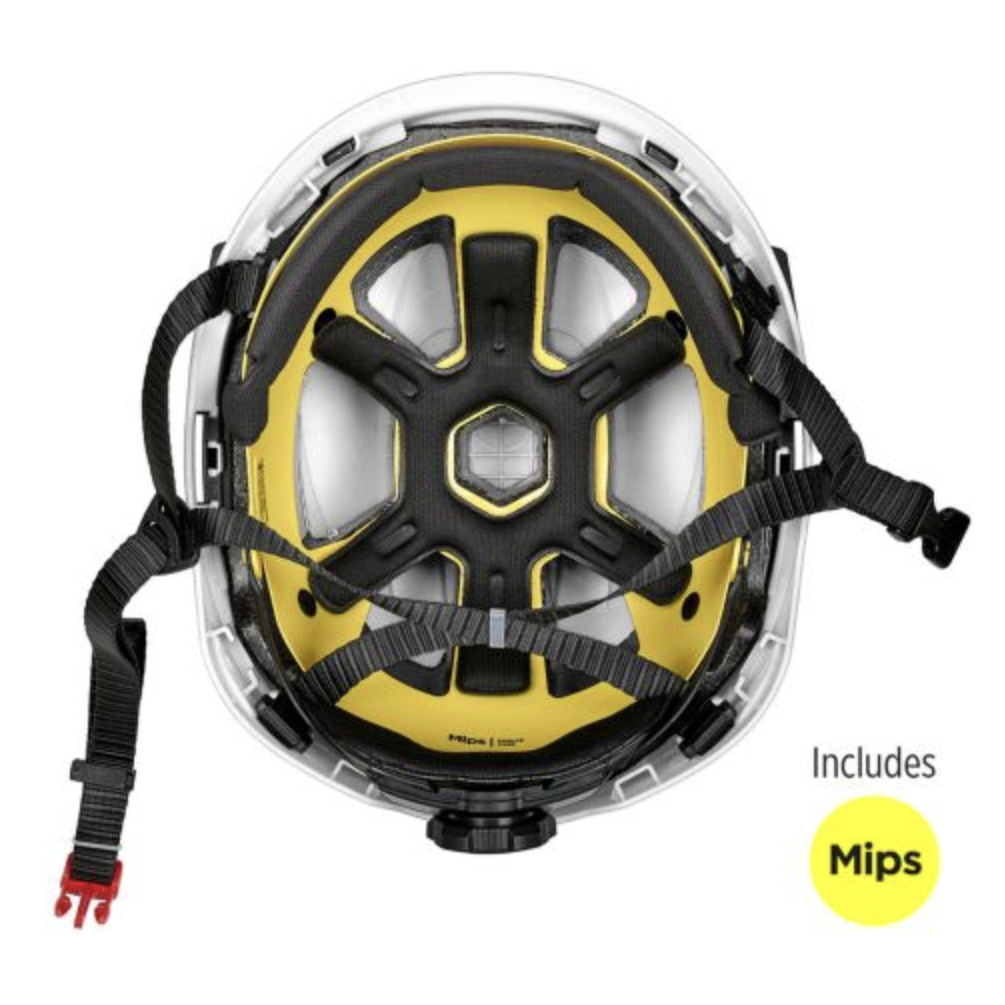
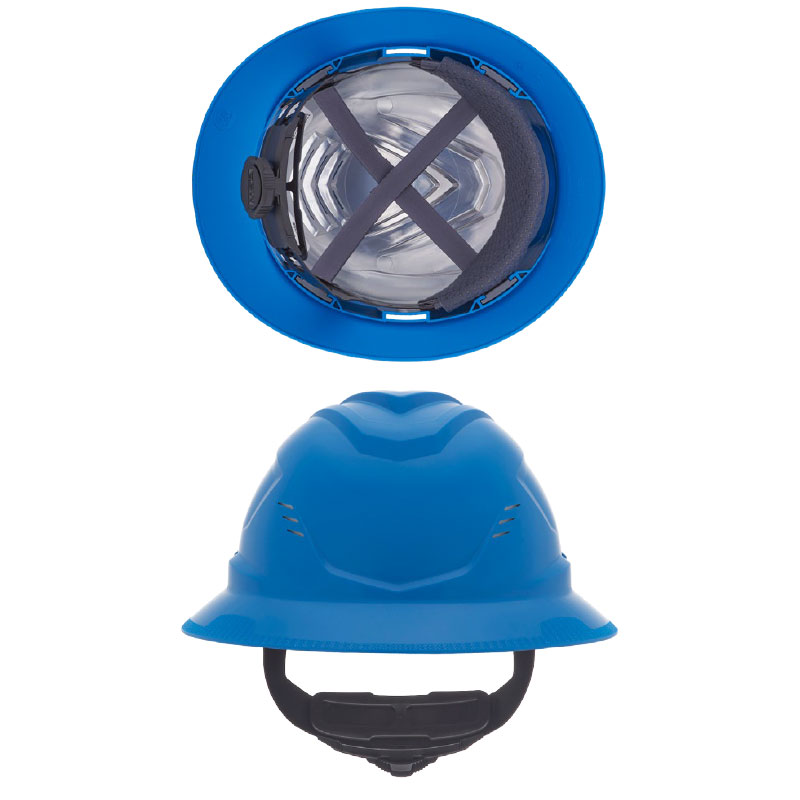
The MSA V-Gard® H2™ Safety Helmet (Type II) comes standard with an integrated chin strap and offers an optional Mips® (Multi-Directional Impact Protection System) layer.
What Mips® means for safety:
Mips is designed to let the helmet’s inner liner move slightly relative to the head during an angled impact. That small shift helps redirect and reduce the rotational forces that can cause serious brain injuries. In practice, it adds another line of defense beyond standard impact protection.
This combination makes the V-Gard H2™ a strong fit for at-height work, vehicle aisles, and busy material-handling zones — anywhere slips, trips, or unexpected contact can turn into dangerous angled impacts.


Heat stress: keep heads cool without compromising protection
When temperatures soar, comfort and compliance drop. Plan for heat the same way you plan for impact protection.
- Choose full ‑brim for added shade and sun protection
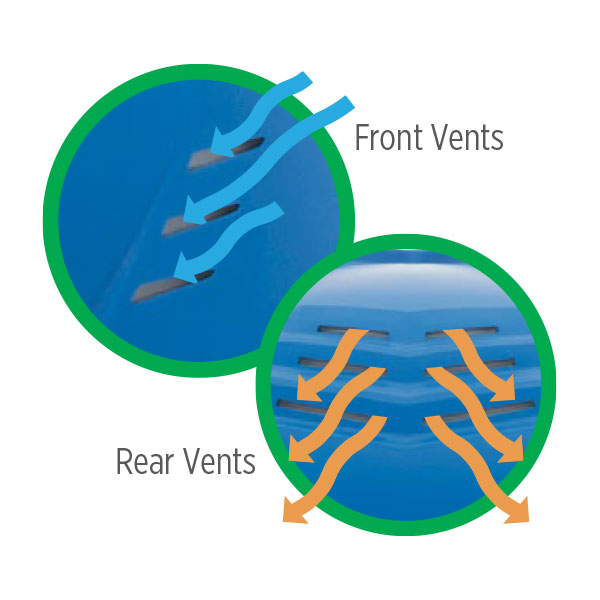
- Use vented shells where there’s no electrical exposure; choose Non vented‑ Class E for energized work
- Look for sweat ‑management features and breathable suspensions
- Consider cooling accessories like a crown cooler or wet cooling pads when appropriate
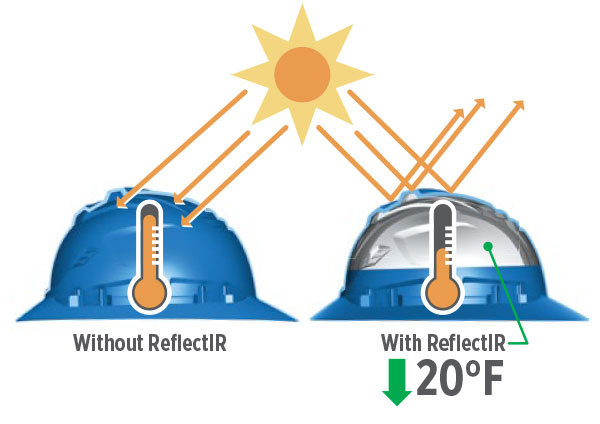
MSA V‑Gard C1® Hard Hat (Type I, full brim) uses ReflectIR™ thermal‑barrier technology to help reduce interior heat in sunny conditions; select vented or non‑vented models based on electrical risk – that can keep the hard hat interior up to 20°F cooler.
Daily use: the 30‑second check
- Shell: no cracks, deep gouges, or UV chalking
- Suspension: not brittle or deformed; correct clearance
- Chin strap: anchors intact; buckle fastens under the chin
- Accessories: only approved mounts; no drilled holes or screws
- Replace if: any significant impact, visible damage, or end of‑ ‑life per the manufacturer
Keep spares on hand so damaged helmets leave service immediately.
Reduce head injuries by following these guidelines:
- At ‑height = helmet + chin strap. Non-‑negotiable for lifts, edges, scaffolds
- Forklift & vehicle lanes: Use Type II for pedestrians/spotters
- No substitutes: bump caps/baseball‑cap inserts are not head protection where helmets are required
- Training: Tie refreshers to quarterly safety days or toolbox talks

How Arbill helps…
We’ll evaluate your tasks and advise which Class Type will work best in your environment. Our EHS Managed Services team of specialists can provide Fall Protection training, PPE evaluation as well as offer additional solutions for heat-mitigation.
I WANT TO LEARN MORE ABOUT ARBILL’S COMPREHENSIVE APPROACH TO SAFETY!
*All fields are required.